Japan
News
27 Apr 2022
Hokkaido University researchers have shown how chronic pain leads to maladaptive anxiety in mice, with implications for treatment of chronic pain-related psychiatric disorders in humans.
26 Apr 2022
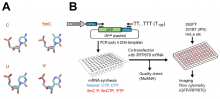
Researchers set out to find new ways to artificially induce mRNA to respond in ways that could eventually lead to therapeutic outcomes, expanding on the success of the mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines and opening up new possibilities across a host of possible genetic therapies.
26 Apr 2022
Using muonic x-rays from a high-energy accelerator and a technology used for astronomical observations, researchers can now see the elemental makeup of sensitive samples without damaging them.
25 Apr 2022
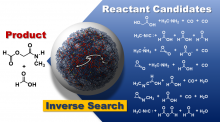
Researchers overcome computational limitations to predict the starting materials of multi-step reactions using only information about the target product molecule.
25 Apr 2022
Examination of endangered species’ stem cells unveils ancient genetic links between mammals.

25 Apr 2022
A recent infant study suggests that the visual experience in daily life contributes to the emergence of upper visual field bias for faces.
22 Apr 2022
Scientists discovered that intramuscular fat levels are indicative of heart health. Measurements of intramuscular fat in 93 heart failure patients’ thighs showed patients with high intramuscular fat levels were at greater risk of rehospitalisation, despite no significant differences in conventional heart health criteria. These findings enable new approaches for treating heart failure, a growing concern in Japan’s ageing society.
21 Apr 2022
A porous material, which opens to receive highly flammable acetylene and closes to release it, sidesteps the flaws of the existing storage method.
21 Apr 2022
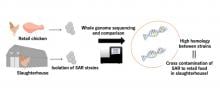
Genome profiling of Staphylococcus argenteus strains unveiled cross-contamination among Japanese retail foods and slaughterhouses.
20 Apr 2022
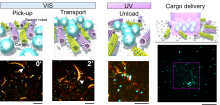
In a global first, scientists have demonstrated that molecular robots are able to accomplish cargo delivery by employing a strategy of swarming, achieving a transport efficiency five times greater than that of single robots.
20 Apr 2022
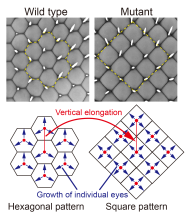
Tile patterns in which the same shape is laid out without gaps are found in the compound eyes of insects. Hexagonal tile patterns are common while shrimp eyes have a square pattern. We investigated tile pattern formation using Drosophila and revealed that the compound eye tile pattern is controlled by a geometrical division mechanism, Voronoi tessellation, in addition to physical constraints determined by the combination of the regular distribution and growth of the individual eyes.
18 Apr 2022
In disaster mitigation planning for future large earthquakes, seismic ground motion predictions are a crucial part of early warning systems. The way the ground moves depends on how the soil layers amplify the seismic waves (described in a mathematical site “amplification factor”). However, geophysical explorations to understand soil conditions are costly, limiting characterization of site amplification factors to date. Using data on microtremors in Japan, a neural network model can estimate site-specific responses to earthquakes based on subsurface soil conditions.

13 Apr 2022
• Effects of gestational bisphenol A exposure were compared between rat dams and their offspring.
• Bisphenol A affected the dams' circadian rhythm, immune response, and insulin resistance.
• Nevertheless, at the multi-omics levels (transcriptome and lipidome), the impact on the dams was less than on their offspring.
• Multi-variates analysis successfully differentiated the multi-omics effects between dams and their offspring.

13 Apr 2022
Helping solve social and global environment issues with agriculture, forestry, and oceanography research combined with the latest technologies
12 Apr 2022
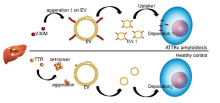
Researchers at Kanazawa University elucidate in Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences how small biocontainers enclosed by membranes are involved in a disease called ATTRv amyloidosis.
11 Apr 2022
Milling rice to separate the grain from the husks, produces about 100 million tons of rice husk waste globally each year. Scientists searching for a scalable method to fabricate quantum dots have developed a way to recycle rice husks to create the first silicon quantum dot LED light. Their new method transforms agricultural waste into state-of-the-art light-emitting diodes in a low-cost, environmentally friendly way.
08 Apr 2022
A team of international researchers, led by Associate Professor Masaki Eda of the Hokkaido University Museum, have discovered that the oldest type of poultry ever domesticated may have been geese. The study involved interdisciplinary research of bones excavated from Tianluoshan site in the lower Yangtze River valley, Zhejiang Province, China.
07 Apr 2022
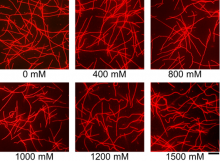
The molecule trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) can be used to reversibly modulate the rigidity of microtubules, a key component of molecular machines and molecular robots.
06 Apr 2022
Climate changes in the tropical Pacific have temporarily put the brakes on rapid warming and ice melting in Greenland.
06 Apr 2022
Osaka City University* study suggests memories are formed through an integration across brain regions via burst activity in amygdala-prefrontal neuronal ensembles during memory acquisition, and then hippocampal-prefrontal synchrony during post-experience sleep. (Osaka City University has now changed its name as Osaka Metropolitan University)
05 Apr 2022
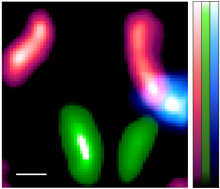
Researchers have captured images of cells in mice using astronomy technology
04 Apr 2022
Distinguished Professor Hiroki Shirato of Hokkaido University is one of the nine recipients of the Japan Academy Prize in 2022, for his groundbreaking work on “Biomedical and Engineering Research about Real-time Tumor Tracking Radiotherapy/Particle Beam Therapy against Cancer.”
04 Apr 2022
伝統的な日本の大学のカルチャーの殻を破り、フラットで国際的な研究所として注目を集める東京工業大学地球生命研究所(ELSI)。今年で10年目を迎えたELSIの魅力や運営のコツについて廣瀬敬前所長が語った。
04 Apr 2022
東京工業大学地球生命研究所(ELSI)は、エビデンスに基づくアウトリーチを展開することで、科学コミュニケーション専門トレーニングの大切さを積極的に発信している。日本の高等教育機関と研究機関での研究アウトリーチ活性化の先駆けとなることを目指す。
31 Mar 2022
Gene editing technology has been used to pinpoint new molecular targets for treating an aggressive form of leukemia in adults.
30 Mar 2022
Researchers have discovered argon trapped in air-hydrate crystals in ice cores, which can be used to reconstruct past temperature changes and climate shifts.
30 Mar 2022
A team led by a Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo researcher has created a model to probe the role of emergent elastic fields in chiral molecular crystals
29 Mar 2022
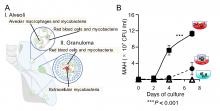
Mycobacteria are a group of pathogenic bacteria that cause diseases like leprosy and tuberculosis in humans. Now, a new study by scientists at Hiroshima University finds that mycobacteria are associated with red blood cells at lung infection sites, an interaction that has escaped scientific notice for 140 years since the discovery of the organism causing tuberculosis.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
Giants in history
Ruby Sakae Hirose (1904 – 1960) was a Japanese-American scientist whose research contributed significantly to our understanding of blood clotting, allergies and cancer.
Haisako Koyama (1916 – 1997) was a Japanese solar observer whose dedication to recording sunspots – cooler parts of the sun’s surface that appear dark – produced a sunspot record of historic importance.
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Toshiko Yuasa (11 December 1909 – 1 February 1980) was the first Japanese female physicist whose research on radioactivity shed light on beta decay – the process in which an atom emits a beta particle (electron) and turns into a different element.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) and Tsuneko (7 June 1933) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Tsuneko (7 June 1933) and Reiji Okazaki (8 October 1930 – 1 August 1975) were a Japanese couple who discovered Okazaki fragments – short sequences of DNA that are synthesized during DNA replication and linked together to form a continuous strand.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Hideki Yukawa (23 January 1907 – 8 September 1981) was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1949 for predicting the existence of the pi meson subatomic particle. Japan’s first Nobel laureate, Yakawa also expressed his support for nuclear disarmament by signing the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955.
Shinichiro Tomonaga (31 March 1906 – 8 July 1979), together with Richard Feynman and Julian Schwinger, was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965, for their contributions to advance the field of quantum electrodynamics. Tomonaga was also a strong proponent of peace, who actively campaigned against the proliferation of nuclear weapons and promoted the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
Japanese chemist Kenichi Fukui (4 October 1918 – 9 January 1998) was the first Asian scientist to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Together with Roald Hoffman, he received this honour in 1981 for his independent research into the mechanisms of chemical reactions.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Japanese physicist Ukichiro Nakaya (1900-1962) made the world’s first artificial snowflakes. He started his research on snow crystals in the early 1930s at Hokkaido University, where there is an unlimited supply of natural snow in winter. By taking over 3,000 photographs, he established a classification of natural snow crystals and described their relationship with weather conditions.
The techniques that make industrial pearl culturing possible were developed over a century ago at the Misaki Marine Biological Station in Japan. The station’s first director, Professor Kakichi Mitsukuri, emphasized to Kokichi Mikimoto in 1890 that stimulating pearl sac formation was important for pearl growth, and they went on to successfully develop methods for culturing pearls.
The field of solid-state ionics originated in Europe, but Takehiko Takahashi of Nagoya University in Japan was the first to coin the term ‘solid ionics’ in 1967. ‘Solid-state ionics’ first appeared in 1971 in another of his papers, and was likely a play on ‘solid-state electronics’, another rapidly growing field at the time.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Motoo Kimura (13 November 1924 – 13 November 1994) was a Japanese theoretical population geneticist who is best remembered for developing the neutral theory of molecular evolution.
Osamu Shimomura (27 August 1928 – 19 October 2018) was a Japanese organic chemist and marine biologist who dedicated his career to understanding how organisms emitted light.
Kikunae Ikeda (8 October 1864 – 3 May 1936) was a Japanese chemist who discovered the fifth basic taste, umami.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Kono Yasui (16 February 1880 – 24 March 1971) was a Japanese botanist who researched the genetics of poppies, corn and spiderworts and surveyed the plants that had been affected by the nuclear fallout after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Hitoshi Kihara (1893 – 1986) was one of the most famous Japanese geneticists of the 20th century. One of his most significant contributions was identifying sex chromosomes (X and Y) in flowering plants.
Michiyo Tsujimura (17 September 1888 – 1 June 1969) was a Japanese agricultural scientist and biochemist recognized for her research of green tea components.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Japanese geochemist Katsuko Saruhashi developed the first method and tools for measuring carbon dioxide in seawater