Chemistry
News
02 Jun 2023
Researchers at Tohoku University and Tsinghua University have introduced a next-generation model membrane electrode that promises to revolutionize fundamental electrochemical research.
01 Jun 2023
Fragments of spherical ‘Buckyball’ molecules have stable electron-accepting ability with great practical potential.
26 May 2023
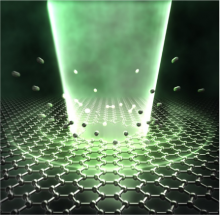
Graphene has revolutionized materials science since its discovery in 2004, with its high electron mobility, mechanical strength, and thermal conductivity. But processing graphene at the micro/nanoscale is a challenging process that often involves large-scale equipment and complex operations. Now, Tohoku University researchers have applied their simple femtosecond laser technique to ultra-thin atomic layers of graphene, resulting in multi-point hole drilling without damaging the graphene film.
25 May 2023
A group of researchers from universities in Thailand and Malaysia have collaborated to develop a unique kind of film that is good for the environment and can decompose naturally. They made this film using leftover pineapple stems, which helps reduce the use of harmful plastic films. This new film has the potential to be used as packaging material, contributing to a more sustainable way of doing business and promoting a circular economy.
23 May 2023
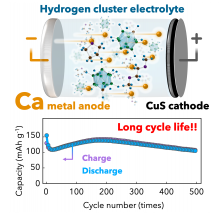
With the use of electric vehicles and grid-scale energy storage systems on the rise, the need to explore alternatives to lithium-ion batteries has never been greater. Tohoku University researchers have recently developed a prototype calcium metal rechargeable battery capable of 500 cycles of repeated charge-discharge - the benchmark for practical use. The breakthrough was made thanks to the development of a copper sulfide nanoparticle/carbon composite cathode and a hydride-based electrolyte.
19 May 2023
Researchers at the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo, use artificial intelligence to help interpret data generated by material science spectroscopy experiments, which can aid in the development of new drugs and organic conductors.
18 May 2023
It’s not unusual for many of us to reach for a cup of coffee or cup of tea whilst focusing our attention on a screen. Scientists have long pondered whether our hand movements influence our spotlight attention. And now a group of researchers from Tohoku University have discovered that our spotlight attention and the attention paid to our moving hands operates via independent mechanisms.
16 May 2023
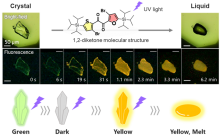
Researchers at Osaka University discovered a new class of photo-responsive crystal compounds, heteroaromatic 1,2-diketones. Certain light irradiation causes the crystals in these materials to melt, dramatically changing the materials’ properties. One member of this class, SO, shows luminescent changes while melting, which enabled the research team to visualize the crystal-melting process at the molecular level. These findings provide fundamental insights into the mechanisms behind crystal melting and will enable future designs of light-responsive materials.
15 May 2023
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) high-speed atomic force microscopy experiments that show how ligands associated with stimulating and suppressing activation of the TRPV1 protein increase and decrease the molecule’s structural variations. The observations provide insights into how these heat- and chilli-sensing proteins function.
12 May 2023
An international research group has developed a new surface coating technology that is capable of significantly increasing electron emission in materials. Their breakthrough is expected to improve the production of high-efficiency electron sources, and lead to increased performances in electron microscopes, electron beam lithography systems, and synchrotron radiation facilities.
12 May 2023
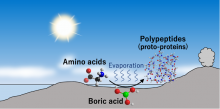
Understanding how catalytic organic polymers emerged on prebiotic Earth is vital to understanding the origin of life. Now, a team of scientists at Tohoku University have recently found a potential environment for the reaction that produced catalytic organic polymers.
11 May 2023
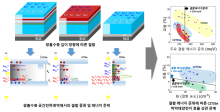
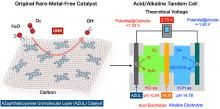
Two undergraduate students publish papers as lead authors in the prestigious international academic journal ChemSusChem, proposing methods to improve eco-friendly hydrogen production through photoelectrochemistry
11 May 2023
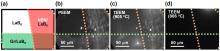
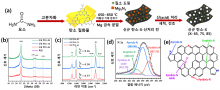
- A joint research team of Yang Kee-Jeong, Kim Dae-Hwan, and Kang Jin-Gyu at DGIST and Kim Jun-Ho at Incheon National University used admittance spectroscopy to suggest a defect energy level in the absorbing layer that deteriorated thin-film solar cell properties
- The research team proposed a defect identification method to ensure high efficiency in thin-film solar cells
09 May 2023
Zinc-air batteries may power the future thanks to their high density, low cost, and nature-friendly makeup. Yet, their low voltage has stymied their widespread application. Now, a research group has realized a zinc-air battery with an open circuit voltage of over 2 V.
09 May 2023
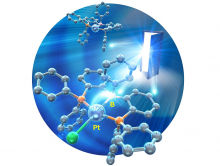
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists elucidated the molecular structure of anionic Pt(0) complexes for the first time in collaboration with co-researchers at Paul Sabatier University - Toulouse III. The key to success is the stabilization of anionic Pt(0) complexes (which are usually unstable owing to their electron-donating nature) by the electron-accepting properties of boron compounds. The results of this research allow us to elucidate the properties and functions of highly active chemical species and provide new guidelines for their creation. The research is expected to lead to the development of innovative catalytic reactions mediated by these chemical species.
01 May 2023
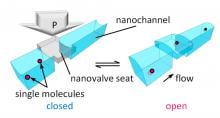
A joint research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has succeeded in regulating the flow of single molecules in solution by opening and closing the nanovalve mounted on the nanofluidic device by applying external pressure. The research group fabricated a device with a ribbon-like, thin, soft glass sheet on the top, and at the bottom a hard glass substrate having nanochannels and nanovalve seats. By applying external pressure to the soft glass sheet to open and close the valve, they succeeded in directly manipulating and controlling the flow of individual molecules in solution. They also observed an effect of fluorescence signal amplification when single fluorescent molecules are confined in the tiny nanospace inside the valve. The effect can be ascribed to the nanoconfinement, which suppresses the random motion of the molecules.
26 Apr 2023
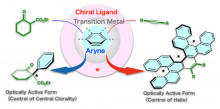
An Osaka Metropolitan University scientist published a review article on numerous asymmetric reactions using arynes, organized by style, and detailed their outline and characteristics. Unresolved issues and prospects in this field were also described.
17 Apr 2023
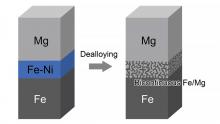
Transport relies heavily on steel. But steel is heavy, and scientists are turning to alternatives to lessen the transportation industry’s carbon emissions. Magnesium alloys are one such alternative. But developing bonding technology that bonds magnesium alloys with structural steels has been severely limited because magnesium and iron are immiscible. Yet, a research group from Tohoku University has established a dealloying bonding technology that obtains a strong mechanical bond between iron and magnesium.
14 Apr 2023
We typically think of robots as metal objects, filled with motors and circuits. But the field of molecular robotics is starting to change that. Like the formation of complex living organisms, molecular robots derive their form and functionality from assembled molecules stored in a single unit, i.e., a body. Yet manufacturing this body at the microscopic level is an engineering nightmare. Now, a Tohoku University team has created a simple workaround.
13 Apr 2023
A research group at Osaka Metropolitan University has succeeded in selectively recovering trace rare earth elements in synthetic seawater and environmental water, such as hot spring water, using baker’s yeast with a phosphate group added. The phosphorylated yeast is expected to be utilized as a material for recovering useful metals and removing toxic metals, thereby contributing to the realization of a metal resource-circulating society.
10 Apr 2023
AI finds the first stars ✨were not alone, Auto-switch for large electronic devices, A metabolite against autoimmune diseases, & Converting fruit waste 🍊🍉into solar stills. Plus in our blog: A career worth doing, a life worth living. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
05 Apr 2023
We sat down with Dr. Ji Ha Lee to get to know her and her work on developing recyclable and degradable gels that can replace plastics as well as nanogels that can help with targeted drug delivery.
31 Mar 2023
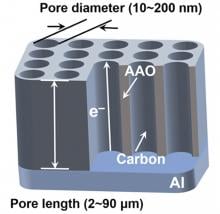
- Development of low-temperature, highly graphitized carbon synthesizing method that can overcome the limitations of existing fuel-cell carbon supports
- Expected to be used in next-generation fuel-cell vehicles with improved generation efficiency and excellent stability
- Study results will be published in ‘Applied Catalysis B: Environmental’, a top journal in the field of Environmental Science
31 Mar 2023
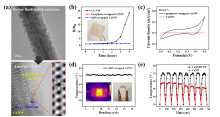
- The world’s first technology for synthesizing high-quality and low-cost copper-graphene nanowire using intense scintillation
- Implementation of high-performance transparent-flexible electronic device based on copper-graphene nanowire and publication in the international journal Nano Energy, which is renowned in the field of energy
29 Mar 2023
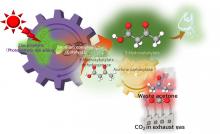
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists have developed a process using artificial photosynthesis to successfully convert more than 60% of waste acetone into 3-hydroxybutyrate, a material used to manufacture biodegradable plastic. The results were obtained using low-concentration CO2, equivalent to exhaust gas, and powered by light equivalent to sunlight for 24 hours. The researchers expect that this innovative way of producing biodegradable plastic could not only reduce CO2 emissions but also provide a way of reusing laboratory and industrial waste acetone.
24 Mar 2023
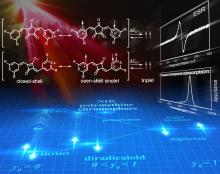
An Osaka Metropolitan University joint research group has discovered that near-infrared absorbing dyes, which had previously been considered to have closed-shell electronic structures, have an intermediate electronic structure, between closed- and open-shell structures. They also found that as the wavelength of near-infrared light that can be absorbed becomes longer the contribution of open-shell forms increases within the dye. These newly discovered characteristics are expected to be utilized to develop new near-infrared absorbing dyes that can absorb longer wavelength near-infrared light.
24 Mar 2023
Scientists in Singapore converted fruit waste into a solar absorber called Mxene to develop an efficient and sustainable water desalination process.
22 Mar 2023
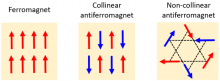
A research team has highlighted recent achievements in antiferromagnetic spintronics in a review article, unearthing a new frontier in the field.
20 Mar 2023
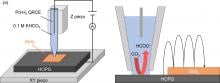
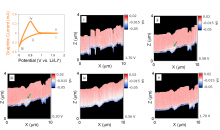
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in JACS Au how they have developed operando scanning ion conductance microscopy to allow simultaneous measurements of changes in the anode surface topography of a lithium ion battery during use, as well as the varying ion concentration with depth. Combining both types of information should help researchers evaluate the correlation between the two to design better batteries.
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Researchers
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Giants in history
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline