Biology Microbiology
News
27 Feb 2024
Applied Microbiology International has announced it will be launching a new series of educational online content called The Microbiologist Masterclass.
07 Feb 2024
Yokohama National University scientists are working towards creating a better tomorrow by addressing diverse challenges, from snow algae and tropical cyclones to AI cyberthreats, and much more.
24 Jan 2024
This week sees the launch of the first published content in Sustainable Microbiology, the new open access journal which will apply microbiology to sustainability. The journal is published by Applied Microbiology International.
30 Nov 2023
A new bacterial species discovered at the deep-sea hydrothermal vent site ‘Crab Spa’ provides a deeper understanding of bacterial evolution.
29 Nov 2023
Mycorrhiza biofertilizer Uttam Superrhiza has been named as the winner of the Applied Microbiology International Product of the Year 2023.
The prestigious prize recognizes a commercial product derived from microbiology research, with special consideration given to those products that have addressed the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
16 Nov 2023
The winners of the Applied Microbiology International Horizon Awards were announced at the prestigious Environmental Microbiology lecture 2023, held at BMA House in London on November 16.
08 Nov 2023
Applied Microbiology International (AMI) has launched its reviewer training scheme for the journal Letters in Applied Microbiology (LAM), building upon its development opportunities for early career scientists in journal publishing.
27 Oct 2023
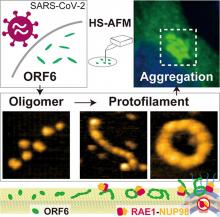
Researchers at Kanazawa University report in the Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters high-speed atomic force microscopy studies that shed light on the possible role of the open reading frame 6 (ORF6) protein COVID19 symptoms.
16 Oct 2023
The shortlist for the Applied Microbiology International Awards 2023 has now been announced.
The AMI Awards programme is designed to celebrate the brightest minds in our field and promote the research, group, projects, products and individuals who continue to help shape the future of applied microbiology.
05 Oct 2023
The finalists in the Applied Microbiology International Product of the Year Award 2023 have been announced. The awards promote the research, groups, projects, products and individuals who are shaping the future of applied microbiology.
19 Jul 2023
Scientists have combined two light wavelengths to deactivate a bacterium that is invulnerable to some of the world’s most widely used antibiotics, giving hope that the regime could be adapted as a potential disinfectant treatment.
01 Jun 2023
Tests could soon identify patients who will respond well to the available treatment for chronic myeloid leukaemia and those who will be resistant to it—which could improve their chances of survival.
25 May 2023
Eating fermented foods might be the secret to a healthy and long-lived society
18 Mar 2023
Scientists restore impaired kidney for the first time, How fibre composite fails when wet, Cleaner fish recognize themselves in pictures 🖼️🐟& The source of black carbon in the sea. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice. Plus our magazine Asia Research News 2023 is out now 🎉!
21 Feb 2023
Sifting through sewage for SARS-CoV-2 genetic material could help authorities tailor infection control policies.
02 Feb 2023
Blocking an immune-regulating protein reverses the damage caused by acute and chronic kidney disease, a preclinical study suggests.
30 Nov 2022
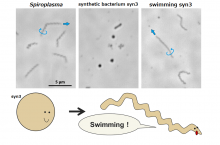
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers introduced seven proteins, thought to let bacteria swim by switching the direction that their helical bodies spiral, into a strain of synthetic bacterium with minimal genetic information. As a result, they confirmed that the synthetic bacterium named syn3, which is normally spherical, formed a helix that could swim by spiraling. Further investigation revealed that only two of these newly added proteins were required to make syn3 capable of minimal swimming. This swimming synthetic bacterium can be said to be the smallest mobile lifeform genetically, as it contains the fewest number of genes.
10 Oct 2022
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant escapes the immune response better than its coronavirus ancestors, but has also facilitated our transition to a society that can live with COVID-19.
15 Sep 2022
Cellular structures called mitochondria depend on microproteins to assist and control the assembly of a protein chain that extracts energy from nutrients, according to a new study by scientists in Singapore.
26 Aug 2022
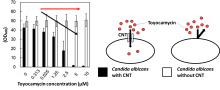
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have clarified that an adenosine analog—the antibiotic toyocamycin—is taken up into cells by a concentrative nucleoside transporter (CNT) in Candida albicans, an opportunistic yeast fungus that causes candidiasis infections. This was also true of the human CNT3 protein. They found that C. albicans CNT and human CNT3 proteins take up similar molecules at different rates depending on their molecular size and structure. These results are expected to lead to the development of new antifungal drugs that are effective only against C. albicans and safe for humans.
05 Jul 2022
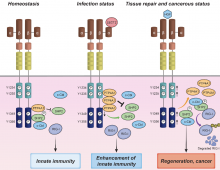
Innate immunity is activated when the pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). We show that a liver-derived secretory protein LECT2, a hepatokine, binds to the HGF receptor MET, a proto-oncogene product, to suppress the proliferation signal of MET. LECT2 activates retinoic acid-inducible gene-I, enhancing antiviral and innate immune responses through MET. Thus, LECT2 is an anti-proliferative and immunoregulatory factor that could be a therapeutic target for viral infections and cancer.
14 Apr 2022
Bacteria hitchhike on red blood cells, New model simulates effects of exercise on muscles, Argon found in air of ancient atmosphere and Revealing emergent elastic fields of chiral crystals. Read all in the April Editor's Choice and this month's Asia Research News 2022 magazine pick - Asia's race to outsmart antimicrobial resistance.
29 Mar 2022
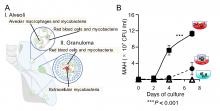
Mycobacteria are a group of pathogenic bacteria that cause diseases like leprosy and tuberculosis in humans. Now, a new study by scientists at Hiroshima University finds that mycobacteria are associated with red blood cells at lung infection sites, an interaction that has escaped scientific notice for 140 years since the discovery of the organism causing tuberculosis.
08 Mar 2022
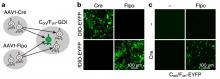
Scientists develop a method to genetically label neurons with a single gene of interest in mice by combining the anterograde transsynaptic spread of adeno-associated virus serotype 1 (AAV1) with intersectional gene expression. In two distinct circuits: the retina/primary visual cortex to the superior colliculus and the bilateral motor cortex to the dorsal striatum, injections of AAV1 expressing either Cre or Flpo recombinases and the Cre/Flpo double-dependent AAV into two upstream regions and the downstream region, respectively, were used to label postsynaptic neurons receiving inputs from the two upstream regions.
22 Feb 2022
A Japanese research team created a new way to sort living cells suspended in fluid using an all-in-one operation in a lab-on-chip that required only 30 minutes for the entire separation process.
31 Jan 2022
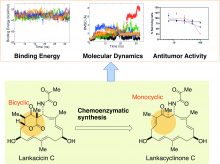
Garden soil houses a variety of bacteria and their natural byproducts — including one that may help halt tumor growth. Lankacidins are molecules that can be isolated from Strepomyces rochei, a common bacterium in soil. In addition to antimicrobial properties, a type of lankacidins, called lankacidin C, can inhibit tumor activity in various cancer cell lines, including leukemia, melanoma, ovarian and breast cancers. Lankacidin C offers a potential foundation on which to design anticancer drugs, but its structure is complicated and difficult to manipulate, according to an international research group. The same group recently identified where antitumor activity is housed on the molecule and has now used that information to simplify lankacidin as a potential starting point to engineer treatments.
27 Sep 2021
The missing link isn’t a not-yet-discovered fossil, after all. It’s a tiny, self-replicating globule called a coacervate droplet, developed by two researchers in Japan to represent the evolution of chemistry into biology.
20 Jul 2021
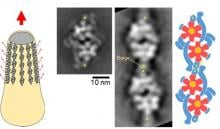
Using electron microscopy and high-speed atomic force microscopy, researchers show the internal molecular motor behind the gliding mechanism for Mycoplasma mobile to consist of two ATP synthase-like molecules. Sharing a similar structure with ATP synthase suggests a common evolutionary ancestor. This synthase-like ATPase is challenging the origin of cells and proteins themselves.
08 Jul 2021
Researchers at The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science use artificial intelligence to predict the size of cells over time without the need for simplifying assumptions, which may lead to a new understanding of microbiology principles and improved drug manufacturing from recombinant bacteria
Events
Sorry, nothing coming up for this discipline
Researchers
Dr Sarkar is a senior research fellow at the Murdoch Children's Research Institute in Melbourne, Australia. She is
actively engaged in collaborating with academic and industry stakeholders and leads multiple projects for the development of novel therapeutics/vaccines to tackle antimicrobial resistance.
Dr Ashfaq Ahmad Shah 'اشفاک ' born on 6 June 1992, from south Kashmir, Doderkoot ددیرکوٹ Kulgam, Jammu and Kashmir, India is the infection immunity doctoral researcher at the Graphic Era (Deemed to be University), Dehradun, UK, India. Dr Shah is pursuing novel dimensions of infection immunity pertaining to the correlation and impact of phyto-immune components termed phytoalexins and phytoanticipins on the benign immune system of human beings. This parameter of immunology is termed phytoalexin-immunomodulation scrutiny. His area of interest lies in Preclinical and clinical studies, i.e. vaccine adjuvant development, development of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial compounds, evaluation of antibiotic resistance, study of Immuno-modulatory activities, disease model studies, protease isolation against specific protein antigens, and the discipline of Kalology including tyrosinase inhibition, PPO inhibition, skin whitening agents, kerato-peeling etc. Dr Ashfaq is a Doctoral Researcher, Reviewer and Editorial member of several journals and books. He is having several publications in journals of national and international repute. So far he has published more than thirty scopus infection/immunology/pharmacology scientific papers, including Fifteen international book chapters and two international books. Mr Shah received the Young scientist award in August 2023 for his groundbreaking academic performance in the field of infection immunity. Mr Shah has also been an editor of Wikipedia pages in medical science since 2015 with more than 1000 edits in medical topics available to medical literature worldwide.
Dr. Cheng-Siang Tan is an Associate Professor at the Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS). He is an expert in infectious and emerging diseases and biosafety and biorisk management.
Dr. Crumlish has researched aquatic microbial diseases, specifically ones that have economic impact in global aquaculture, and potential solutions to such infectious diseases. Her current project seeks to develop vaccines against antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture.
Dr. Tay has researched antibodies and diseases like malaria and SARS-CoV-2 at A*STAR. His focus is on discovering methods for developing antibodies that can be used in therapies against multidrug-resistant pathogens.
Dr. Ikhsan is an associate professor at the Department of Aquaculture, University Putra Malaysia. She specializes in the field of Aquatic Microbial Ecology particularly in the development of innovative and sustainable microbial management strategies through understanding of the host-microbe interaction for enhanced microbial stability.
Dr. Bifani is a principal investigator at A*STAR ID Labs at their Antimicrobial Resistance Lab. He has extensively researched antimicrobial resistance in tuberculosis and malaria. He is also an associate professor and research director at the Yong Yoo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore.
Dr. Deng is a biomedical scientist with a special interest in bacterial virulence, including gene regulation, signaling pathways, and RNA epigenetics. He has worked on virulence regulation in pathogens to discover new therapies against bacterial infections.
Dr. Mitchell is a professor at the Department of Biological Sciences, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST). His primary research interest is the study of bacterial strains that attack and prey on other bacteria, including antimicrobial-resistant pathogens.
Dr. Soojin Jang heads the Antibacterial Resistance Research Laboratory at Institut Pasteur Korea, where her team focuses on discovering new antibacterial agents for “superbugs” or bacteria resistant to most antibiotics.
Department of Microbiology / Biomolecular Sciences
Universiti Teknologi MARA
Malaysia
Myungin Baek is currently an Assistant Professor at Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
Assistant Professor of Environmental Science
Krishna Institute of Allied Sciences
Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences
Deemed To Be University, Karad
Aparna B. Gunjal is a microbiologist at Dr. D.Y. Patil, Arts, Commerce & Science College, India.
Professor Ahmed Al-Haddad, M.Sc., Ph.D. (Germany) is currently Professor of Microbiology and Medical Microbiology at College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Hadhramout University-Yemen.
He is the Founding-Dean of the first Faculty of Nursing in Yemen. He has over fifteen years of research and teaching experience in various domains of life sciences.
Al-Haddad has published many peer reviewed articles and conference papers in the areas of molecular biology, microbiology and antibiotics in National and International journals.
He is reviewer in different national and international Scientific Journals such as Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, Journal of Microbiology and Antimicrobials, Sultan Qaboos University Medical Journal, British Biotechnology Journal.
He is a member of various national and international scientific organizations.
Currently Associate Professor at Universiti Putra Malaysia. Holds a PhD from University College of Wales and BSc (Hons) Genetics from the University of Liverpool
Professor and Head of Microbiology and Immunology Department,
Faculty of Medicine, Lincoln University College (LUC) Malaysia.
Giants in history
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Roseli Ocampo-Friedmann (23 November 1937 – 4 September 2005) was a Filipino-American scientist whose research focused on cyanobacteria and microorganisms that inhabit extreme environments.