Medicine
News
08 Dec 2021
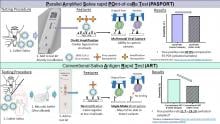
A new saliva-based COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test (ART) technology co-developed by the SingHealth Duke-NUS Academic Medical Centre and the National University of Singapore shows promise in early clinical testing, outperforming existing ARTs and delivering results in minutes, with nearly comparable sensitivity to the gold standard Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) test.
03 Dec 2021
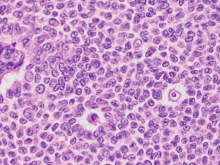
Examination of Japanese cases of gynecological cancer offers a better understanding of the profile of a rare ovarian tumor and could change treatment guidelines.
02 Dec 2021
Giants in History: Esther Park (1877-1910), born Kim Jeom-dong, was the first female Korean physician to practise modern medicine in Korea.
24 Nov 2021
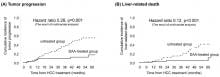
Researchers from the Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine have shown in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma who received cancer treatment that eliminating the hepatitis C virus with a direct-acting antiviral treatment reduces the risk of the liver cancer progression and increases overall patient survival.
23 Nov 2021
Giants in History: Min Chueh Chang (10 October 1908 – 5 June 1991) was a Chinese-American biologist who studied fertilization in mammalian reproduction.
22 Nov 2021
The joint research team of Prof. Hongsoo Choi(DGIST) & Prof. Sung Won Kim(Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital), developed an hNTSC-based microrobot for minimally invasive delivery into the brain tissue via the intranasal pathway
16 Nov 2021
Scientists are turning to genomics to better understand the epidemiology of malaria and to inform control and elimination interventions and strategies. In the Lake Victoria region of Kenya, malaria burden remains very high despite more than a decade of intense control activities. A team of researchers from Osaka City University, Nagasaki University, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and Mount Kenya University generated whole Plasmodium falciparum genome sequences from the lake region. Their analyses revealed that malaria parasites from this region appear distinct from other parasites from East Africa, while frequencies of known drug resistance markers were similar to those in other East African parasite populations. Their findings will help to develop improved surveillance tools to determine parasite transmission routes and aid clinical disease management.
11 Nov 2021
Giants in History: A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
02 Nov 2021
Malfunctioning of the so-called Hippo signalling pathway within animal cells leads to irregular activity of proteins that regulate genes involved in cell proliferation. Researchers have identified a key step in the process of this aberration, opening the door to new therapeutics for cancers such as head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma and lung adenocarcinoma.
02 Nov 2021
The world’s largest analysis of gastric tumour cells provides a launch pad for scientists to plan more effective therapies.
29 Oct 2021
The new radiosensitivity biomarker can make way for chemoradiotherapy treatments tailored to each cancer patient in the future.
27 Oct 2021
Researchers reveal correlation between ribotype (RT) strains of Cutibacterium acnes, which are found in human skin, and the lifespan of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Strains RT4 and 8, which are associated with acne in human skin, shortened the lifespan of the nematode, while RT6, which are predominantly found in healthy human skin, did not. Also, it was found that the healthy skin-related RT6 strain of C. acnes improved C. elegans resistance to the pathogenic organism Staphylococcus aureus.
25 Oct 2021
Researchers have revealed in an animal model that ImmuBalance, a fermented soybean product, is effective in suppressing airway inflammation caused by asthma. Results showed a decreased presence of eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, a decrease in mucus production in the bronchial epithelium, and a suppression of proteins that induce eosinophilic inflammation.
20 Oct 2021
Giants in History: Fe Villanueva del Mundo (27 November 1911 – 6 August 2011) was a Filipina paediatrician who founded the Philippines’ first paediatric hospital. She graduated top of her class at the University of the Philippines, and in 1936 became the first female student to attend Harvard Medical School.
14 Oct 2021
Researchers from The University of Tokyo Institute of Industrial Science describe a novel feature of the immune response to certain viruses such as measles
13 Oct 2021
Giants in History: Tsai-Fan Yu (1911 – 2 March 2007) was a Chinese-American physician and researcher who was the first female full professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine.
13 Oct 2021
Miniature brains mimic critical features of Parkinson's disease, better weather forecasting with satellite data, light does the twist for quantum computing, new insights into embryonic development & elevating women leaders in Myanmar in the October Editor's Choice. Plus don't forget submissions for Asia Research News 2022!
12 Oct 2021
New drug formulations aim to improve the in vivo circulation of Xylonix’s novel immunotherapies for treating both cancer and complications arising from COVID-19 infection.
06 Oct 2021
Giants in History: Wu Lien-teh (10 March 1879 – 21 January 1960) was a Malaysian-born doctor who invented a mask that effectively suppressed disease transmission.
29 Sep 2021
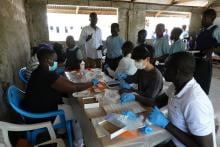
A research team led by scientists at Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) has developed a novel cell sensor with a barcode-like micro-channel structure that enables rapid and low-cost screening of drug-resistant bacteria. The invention could potentially be used on a large-scale in resource-limited situations such as frequent safety screenings of water, food and public facilities, as well as urgent surveys of massive samples during an infectious disease outbreak, particularly in developing countries.
28 Sep 2021
While the Covid-19 pandemic is ongoing, another public health threat, antibiotic resistance, continues unabated. Microbiologists and chemists from two universities in Hong Kong recently made a breakthrough in synthesizing the first vaccine against one of the most deadly antimicrobial resistant pathogens, Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii). The vaccine shows good protection against the superbug in mice, indicating great potential as a vaccine for humans.
24 Sep 2021
Scientists created “elite” antibodies that can beat a broad range of coronavirus strains, including Delta, using a new technique that dramatically speeds up discovering potent antibody candidates.
17 Sep 2021
A specially designed lipid nanoparticle could deliver immune-signaling molecules into liver macrophage cells to overcome resistance to anti-tumor immunotherapy.
13 Sep 2021
iCeMS scientists and colleagues have designed a molecular code that powers up cancer-fighting immune cells.
10 Sep 2021
Magnetic patterns in meteorites, Treating mitochondrial diseases, underwater sensors and a broad COVID-19 vaccine in the September Editor's Choice. Plus, what's it like to communicate vaccine research in a pandemic and Asia Research News 2022.
10 Sep 2021
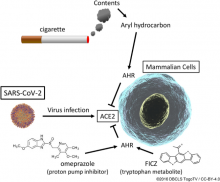
Researchers have identified a potential reason why lower numbers of COVID cases have appeared amongst smokers compared to non-smokers, even as other reports suggest smoking increases severity of the disease.
09 Sep 2021
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba in Japan show that low metabolic flexibility is associated with reduced fat metabolism during sleep.
09 Sep 2021
Researchers from University of Tsukuba in collaboration with Yamagata University scientists find that exposure to light with less blue before sleep is better for energy metabolism. Extended exposure to light during nighttime can have negative consequences for human health. But now, researchers from Japan have identified a new type of light with reduced consequences for physiological changes during sleep.
07 Sep 2021
Recreating major pathological features of Parkinson’s disease in a lab-grown, human mini-brain will help researchers to explore new treatments. This is the first time that Lewy bodies, a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease in patients’ brains, have been produced in the laboratory, offering new insights into the disease.
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Giants in history
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Irene Ayako Uchida’s (8 April 1917 – 30 July 2013) strides to understand genetic diseases such as Down syndrome paved the way for early screening of chromosomal abnormalities in foetuses.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
Maggie Lim (5 January 1913 – November 1995) was a Singaporean physician who promoted family planning and expanded the access to clinics to improve the quality of life for mothers and children in Singapore’s early days.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
The founder of the Adyar Cancer Institute in India, Muthulakshmi Reddy (30 July 1886 – 22 July 1968), fought to uplift women and girls from impoverished situations.
Chinese-American virologist and molecular biologist Flossie Wong-Staal (27 August 1946 – 8 July 2020) was the first scientist to clone HIV and determine the function of its genes.
Maharani Chakravorty (1937 – 2015) was one of India’s earliest molecular biologists whose research paved the way for advances in the treatment of bacterial and viral infections.
Archana Sharma (16 February 1932 - 14 January 2008) conducted research into plant and human genetics that expanded the understanding of both botany and human health. In relation to botany, she uncovered the means by which asexually-reproducing plants evolve into new species.
The first Thai woman to receive a degree in medicine, Margaret Lin Xavier (29 May 1898 – 6 December 1932), is best remembered for her compassion towards her less privileged patients.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Ground-breaking cancer researcher Kamal Jayasing Ranadive (8 November 1917 – 11 April 2001) advanced the understanding of the causes of leukaemia, breast cancer and oesophageal cancer through the use of animal models. She was also among the first to recognise how susceptibility to cancer is linked to tumour-causing interactions between hormones and viruses.
The research of Filipino pharmaceutical chemist Luz Oliveros-Belardo (3 November 1906 – 12 December 1999) focussed on essential oils and other chemicals derived from native Philippine plants.
Thai physician and conservationist Boonsong Lekagul (1907 – 1992) made major contributions to the preservation of his country’s wildlife.
Indian scientist and physician Upendranath Brahmachari (19 December 1873–6 February 1946) is best known for creating a drug called Urea Stibamine, used to safely and reliably treat visceral leishmaniasis (or Kala-azar), a severe infection caused by the Leishmania parasite.
Filipino chemist and pharmacist Manuel A. Zamora (29 March 1870 – 9 July 1929) is best remembered for his discovery of the tiki-tiki formula to combat beriberi, a disease caused by Vitamin B1 deficiency.
Korean parasitologist Seung-Yull Cho (16 November 1943 – 27 January 2019) is remembered largely for his pioneering works to control infections caused by helminthic parasites and his contribution to journal publishing.
Fe Villanueva del Mundo (27 November 1911 – 6 August 2011) was a Filipina paediatrician who founded the Philippines’ first paediatric hospital.
After witnessing death and suffering as a youth in his home village during World War II, Nguyễn Tài Thu (6 April 1931 – 14 February 2021) set his sights on alleviating pain by becoming a doctor. After studying Traditional Chinese Medicine in China in the 1950s, Thu returned to Vietnam to serve in military hospitals. Eventually, he became the country’s foremost practitioner of acupuncture, a technique he first learned by inserting needles into himself.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Wu Lien-teh (10 March 1879 – 21 January 1960) was a Malaysian-born doctor who invented a mask that effectively suppressed disease transmission. Winning the prestigious Queen’s Scholarship enabled Wu to become the first Chinese student to study medicine at the University of Cambridge.
David T. Wong (born 1936) is a Hong Kong-born American neuroscientist who is best known for discovering the antidepressant drug fluoxetine, better known as Prozac.
Indian organic chemist Asima Chatterjee (1917 to 2006) studied the medicinal properties of plant products, especially compounds known as vinca alkaloids.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Salimuzzaman Siddiqui (19 October 1897 – 14 April 1994) was an artist and chemist from Pakistan whose research focused on natural products from plants.
Barry Paw (29 August 1962 – 28 December 2017) was a biologist and oncologist who discovered several novel genes and their functions in red blood cells.
Syed Qasim Mehdi (13 February 1941 – 28 September 2016) was a Pakistani molecular biologist who was a founding member of the Human Genome Diversity Project (HGDP), which assessed human diversity by studying human migration, mutation rates, relationships between different populations, genes involved in height and selective pressure.
Tsai-Fan Yu (1911 – 2 March 2007) was a Chinese-American physician and researcher who was the first female full professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. She discovered that gout, a condition characterized by the painful inflammation of joints, was caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream.
Min Chueh Chang (10 October 1908 – 5 June 1991) was a Chinese-American biologist who studied fertilization in mammalian reproduction.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Esther Park (1877-1910), born Kim Jeom-dong, was the first female Korean physician to practise modern medicine in Korea and trained the first generation of Korean female doctors.