Medicine
News
18 May 2023
It’s not unusual for many of us to reach for a cup of coffee or cup of tea whilst focusing our attention on a screen. Scientists have long pondered whether our hand movements influence our spotlight attention. And now a group of researchers from Tohoku University have discovered that our spotlight attention and the attention paid to our moving hands operates via independent mechanisms.
17 May 2023
To improve the therapeutic techniques to treat those with brain disorders, researchers have developed microscopic, thermally-drawn microelectronic fiber-based neural probes as a means to manipulate both electrical and chemical signals in the brain. Now, a researcher from Tohoku University’s Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences has led a group that increased the functionality of these fibers by equipping them with neurochemical sensing aptamers.
11 May 2023
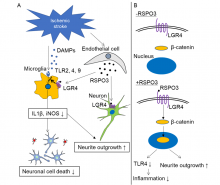
Researchers from Osaka University identified a new protein, R-spondin 3 (RSPO3), that has beneficial effects after ischemic stroke in mice. Specifically, RSPO3 activates the protein LGR4 to trigger a cascade of cellular reactions that decreases inflammation and stimulates the growth of neuronal extensions. Moreover, administrating RSPO3 to mice one day after stroke improved recovery of sensory and motor functions. These findings provide a new target for developing treatments to improve recovery after ischemic stroke.
11 May 2023
Researchers from Osaka University identified a new protein, NICOL, and described its crucial role in the maturation of sperm, which itself is necessary for male fertility. Mice who lacked this protein were sterile. Such a discovery may have implications for the development of male contraceptives.
08 May 2023
Osaka Metropolitan University scientists investigated the prevalence of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in 678 bacterial isolates from 428 companion dogs and 74 companion cats at the Veterinary Medical Center, Osaka Metropolitan University. Two E. coli strains have both a mobile colistin-resistant mcr gene and a third-generation cephalosporin-resistant blaCTX gene. One of these strains, which is found in a dog, was resistant to both colistin and third-generation cephalosporins.
04 May 2023
HKBU joint research suggests that urine cytomegalovirus test facilitates early prediction of AIDS end-organ diseases
28 Apr 2023
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, in particular, lower the prognosis of ischemic strokes by causing inflammation in the brain.
17 Apr 2023
Asia Research Newsは同所の女性研究者5名に、彼女らの研究について、そしてなぜKavli IPMUを選んだのか、これまでの同所での経験について話しを聞いた。それぞれ様々な背景を持ち、各分野で卓越している研究者らに、足かせのない女性がいかに飛躍できるかをみせてもらった。
14 Apr 2023
We typically think of robots as metal objects, filled with motors and circuits. But the field of molecular robotics is starting to change that. Like the formation of complex living organisms, molecular robots derive their form and functionality from assembled molecules stored in a single unit, i.e., a body. Yet manufacturing this body at the microscopic level is an engineering nightmare. Now, a Tohoku University team has created a simple workaround.
10 Apr 2023
Doctors at King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital have developed lightweight and easy-to-use Parkinson's gloves that can automatically reduce tremors, allowing patients to enjoy social life and reducing side effects from medication and risk from brain surgery.
10 Apr 2023
AI finds the first stars ✨were not alone, Auto-switch for large electronic devices, A metabolite against autoimmune diseases, & Converting fruit waste 🍊🍉into solar stills. Plus in our blog: A career worth doing, a life worth living. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice.
10 Apr 2023
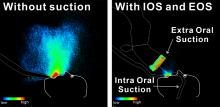
The COVID-19 pandemic has made us more aware of the aerosols that hang around in the air and spread certain infectious diseases. Common dental procedures can be potentially hazardous in this regard. Therefore, it is crucial for researchers to be able to measure how aerosols spread so they can reduce them. A recent study harnessed a high-sensitivity camera and a high intensity LED light source, along with a mannequin and dental air turbine, to measure the spread of aerosols and the effectiveness of various means to reduce them.
07 Apr 2023
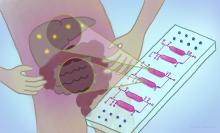
A tiny platform empowers scientists to examine how gut and liver cells interact in health and disease.
05 Apr 2023
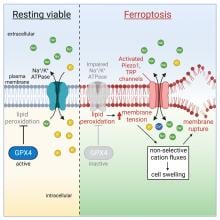
Ferroptosis is a recently discovered type of cell death associated with certain neurodegenerative, cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Whilst scientists have understood that accumulated iron and degenerated lipids trigger ferroptosis, the actual mechanisms at play have remained a mystery. A team of researchers from Tohoku University has identified where in the cells these accumulations take place, and what gets targeted as ferroptosis occurs.
05 Apr 2023
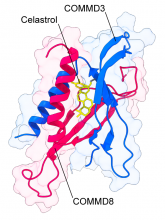
Researchers from Osaka University found that the COMMD3/8 complex is implicated in the progression of the autoimmune response in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. They identified celastrol, the active compound of a medicinal herb, as an inhibitor of the COMMD3/8 complex. Celastrol blocked the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Thus, celastrol is a potential lead for developing treatments against rheumatoid arthritis.
28 Mar 2023
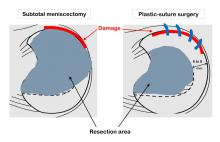
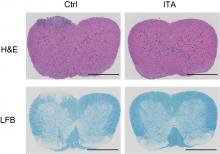
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Medicine conducted an interoperative comparison of lateral disc meniscus injuries of young patients (aged 15 or less), that were treated with plastic sutures or subtotal resection, to see if there was a difference in postoperative cartilage degeneration. The research group observed that sub-total meniscectomies were more likely to show cartilage degeneration, being worst in lateral disc meniscus injuries. In addition, they found that even with higher levels of meniscus damage, preserving the meniscus with sutures was more effective in protecting the cartilage in young patients.
27 Mar 2023
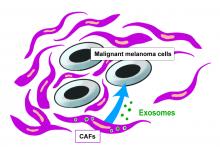
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are key factors in the tumor microenvironment, which have been implicated in cancer cell progression. It has also been reported that vesicles called exosomes produced by these CAFs play an important role in cancer progression. An Osaka Metropolitan University research group investigated the effect of CAF-derived exosomes on the growth of malignant melanoma cells. They found that CAF-derived exosomes express CD9 and CD63 transmembrane proteins, and that the CD9-positive exosomes may inhibit the growth of malignant melanoma cells.
24 Mar 2023
Hailey-Hailey disease is a rare, inherited condition characterized by patches of blisters appearing mainly in the skin folds of the arm pits, groin and under the breasts. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that codes for a specific protein. Tohoku University scientists have uncovered some critical details of this protein’s structure, and the findings could build the foundation for developing treatment for Hailey-Hailey disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
23 Mar 2023
A research group from Osaka Metropolitan University investigated the relationship between tobacco use, including heated tobacco products, with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19. The researchers administered an online survey of living conditions in February 2022 to 30,130 participants aged 16-81 years, finding that heated tobacco product users had significantly higher rates of SARS-CoV-2 infection compared to non-tobacco users. Furthermore, the research group found that among all tobacco users, those who used both heated tobacco products and traditional cigarettes had the highest incidence of requiring hospitalization or oxygen due to COVID-19.
20 Mar 2023
Scientists from Alliance University, Bangalore, Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Inha University, Hanyang University, South Korea, and Newcastle University in Singapore have developed a new and straightforward approach to turn used COVID-19 facemasks into potential absorbent materials that can be employed for carbon capture from atmosphere.
20 Mar 2023
A study led by scientists from Hong Kong Baptist University (HKBU) has identified a protease called MT1-MMP that is a major host factor behind the infectivity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the human body, which leads to the infection of COVID-19 and multi-organ failure. By applying a humanised antibody called 3A2 that can inhibit the activity of MT1-MMP, the viral load of infected mice was reduced by almost 90%. The research team also demonstrated that the protease is a potential therapeutic target for COVID-19.
18 Mar 2023
Scientists restore impaired kidney for the first time, How fibre composite fails when wet, Cleaner fish recognize themselves in pictures 🖼️🐟& The source of black carbon in the sea. Read all in the latest Editor's Choice. Plus our magazine Asia Research News 2023 is out now 🎉!
17 Mar 2023
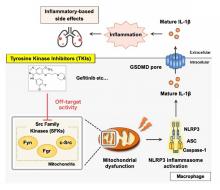
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) are employed to attack specific types of cancer cells. The downside to using TKs is that they can cause serious inflammation. A team of researchers has discovered the underlying mechanism that causes this inflammation.
16 Mar 2023
PAXLOVID™ rollout continues with Laos, Malawi, Rwanda and Zambia as international access to oral treatments improves.
15 Mar 2023
Researchers have revealed the modulatory effect of the anti-inflammatory metabolite itaconate on T helper and T regulatory cells, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches to treating some autoimmune diseases.
14 Mar 2023
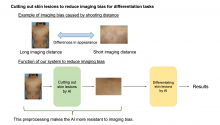
Atopic dermatitis skin lesions and the lesions produced by infectious complications of the disease look so similar that it makes it impossible for patients to spot the difference and know when to visit their doctor for treatment. But an AI-powered mobile app developed by dermatologists now puts the power of diagnosis in the hands of patients.
13 Mar 2023
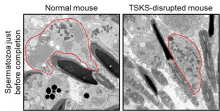
Researchers from Osaka University identified the role of a protein known as testis-specific kinase substrate (TSKS) in the process of spermiation, the release of mature sperm. Analysis of a gene-modified mouse model in which TSKS is disrupted revealed that TSKS is necessary for sperm to eliminate cytoplasm and become streamlined. These findings may lead to the development of diagnostic tests and male contraceptives.
07 Mar 2023
Asia Research News met five female researchers to learn about their research, what drew them to Kavli IPMU, and their experiences there. These women, from diverse backgrounds, excel in their fields and show what can be achieved when women are not held back.
07 Mar 2023
Researchers in Sarawak, Malaysia, measured the immunity responses of people who received different COVID-19 vaccines.
04 Mar 2023
Scientists have shown that swarming molecular robots can deliver cargo five times more efficiently than a robot working on its own.
Events

28 Aug 2014
GIL 2014 New Zealand will bring give you innovative ideas, perspectives and solutions for you to stay ahead of the curve. Held for the first time in New Zealand, the Frost & Sullivan New Zealand Excellence Awards recognises companies across industries within various sectors.

22 Aug 2014
A combined event of the 28th Scientific Meeting of The Malaysian Society of Pharmacology & Physiology (MSPP), the 13th Symposium on Vascular Neuroeffector Mechanisms (VNEM), the 6th Scientific Meeting of The Asian Society for Vascular Biology (ASVB) and The Malaysian Society of Hypertension (MSH).

10 Jun 2014
The event will cover topics like The Next Big Thing - Cover Stories Of News In 2020, top 50 technologies, the future of telecoms, IT, Healthcare and Smart Cities amongst other topics.

20 Feb 2014
Frost & Sullivan's 2014 APAC and Australia Healthcare Outlook and its Impact on Industry Dynamics will take place on Thursday, 20th February 2014 at 9:15 am – 12:00 pm at The Hilton Hotel Sydney, Australia.

18 Feb 2014
The keynote lecture will be on “Making Molecular Prosthetics with a Small Molecule Synthesizer”

13 Nov 2013
SAVE THE DATE!
Malaria, Dengue, Polio, Parasitic Worms, Tick-borne Disease Research Highlights in Washington DC

20 May 2013
Following the tradition of previous meetings, “Brain 2013” will cover numerous aspects within the area of neuroscience research, particularly those related to brain function and metabolism, cerebral blood flow, the function of the neurovascular unit and the blood-brain barrier, brain imaging, and cerebrovascular pathology.

04 Feb 2013
Southeast Asia have amongst the highest level of resistance in the world and is likely to increase in coming years. The primary objective of this meeting is to bring together researchers and clinicians involved in infectious diseases prevention and control.

26 Aug 2012
Congress Theme: 'Beyond the Limit of Histochemistry'

01 Oct 2012
Translating public health research into practice.
1-2 October 2012, Grand Copthorne Waterfront Hotel, Singapore

18 Feb 2012
The Global Health Research Initiative (GHRI) and the Canadian Coalition for Global Health Research (CCGHR) are pleased to present an interactive workshop on global health research career paths at the 2012 annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).

12 Jun 2012
The conference programme will focus on current advances in the science and research of probiotics, prebiotics and their present and future role in maintaining health and preventing diseases.
03 Nov 2011
This congress showcases the latest progress in Nanomedicinal R&D. It will take place in Shenzhen, China from 3rd – 5th November.
30 Nov 2011
The Asian BioCeramics Symposium is held annually to encourage interest in bioceramics and related fields. It will be held in Tsukuba, Japan on the 30th November to 2nd December.

08 Sep 2011
The Royal Society of Chemistry, in collaboration with A*STAR’s Institute of Chemical and Engineering Sciences, GlaxoSmithKline R&D, and with support from the British High Commission in Singapore are organising a symposium on “Contemporary Strategies and Practices in Medicinal Chemistry”.

22 Nov 2011
The first UK-Israel Regenerative Medicine Conference will bring together leading researchers from both countries in the field of regenerative medicine to share latest developments in the field.

03 Nov 2011
2011 International Symposium on Bioelectronics and Bioinformatics (ISBB2011) will be held in the great city of Suzhou, China on 3-5 November, 2011.

28 Sep 2011
The 9th Malaysia Genetics Congress themed “Appreciating the richness of nature through genetics” will be held from 28th to 30th September 2011 at Pullman Hotel, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia.

22 Feb 2011
The 1st Regional Health Sciences and Nursing Conference 2011 will bring together mainstream health professionals, academicians as well as health practitioners to address the latest in knowledge and research in order to find ways to collaborate and work together in order to provide the best possible care in Malaysia.

25 Apr 2011
BIT’s 2nd Inaugural Symposium on Enzymes & Biocatalysis-2011 (SEB-2011) will be held during April 25-29, 2011, Dalian, China.

05 Aug 2010
Scientific workshop focusing on scientific matchmaking, identifying opportunities for collaboration and forming consortia to bid into FP7 funding calls

25 Mar 2010
Three experts of IP & Technology Transfer in the forefront medical field, such as regenerative medicine are invited from US. What are challenges and problems typical in this field? What’s the strategy of prosecution and commercialization in this field? Speech and discussion are expected.

04 Nov 2009
The conference will be organized by a large number of organizations including Abyad Medical Center, Middle East Association on Age, Ageing & Alzheimer's-MEAAA, The Health Ministers' Council for the Cooperation Council States, Lebanese order of physicians-Tripoli-Lebanon and others

15 May 2010
WCIT is a focused conference to present and deliberate the advances in immunology, which is significant, timely and important to the health of humanity. The well selected topics cover across disciplinary breaking, from concept to therapy.

09 Aug 2009
The 9th International Congress on AIDS in Asia and the Pacific will bring people from various backgrounds in Asia and the Pacific region to meet and share knowledge, skills, ideas, research findings related to HIV and AIDS.

31 Jul 2010
BIT’ s 1st World Congress of Virus and Infections-2010 (WCVI-2010) will be held during July 31-August 3, 2010 in Busan, Korea, with a theme of “Voice of Virologists”.

24 Mar 2010
This Congress will present topics concerning the very current advancements in antibody research and product development.

08 Jun 2009
Singapore - World Vaccine Congress Asia 2009, will bring together global and regional vaccine buyers and sellers, regulators, investors, technology and service providers to discuss best business strategies in accessing different vaccine markets in Asia and forging strategic partnerships for international success.

27 Jul 2009
Scientific experts meeting focusing on scientific matchmaking and identifying opportunities for collaboration and to form consortia to bid into upcoming FP7 calls
Researchers
Sorry, no researchers coming up for this topic.
- « first
- ‹ previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Giants in history
Michiaki Takahashi (17 February 1928 – 16 December 2013) was a Japanese virologist who developed the first chickenpox vaccine.
Irene Ayako Uchida’s (8 April 1917 – 30 July 2013) strides to understand genetic diseases such as Down syndrome paved the way for early screening of chromosomal abnormalities in foetuses.
Baron Kitasato Shibasaburo (29 January 1856 – 13 June 1931) was a Japanese physician and bacteriologist whose work led to a new understanding of preventing and treating tetanus, diphtheria and anthrax.
Maggie Lim (5 January 1913 – November 1995) was a Singaporean physician who promoted family planning and expanded the access to clinics to improve the quality of life for mothers and children in Singapore’s early days.
By isolating soil microorganisms and studying the compounds they produce, Satoshi Omura (born 1935) discovered almost 500 organic compounds with unique properties that were produced by these microorganisms, including many new antibiotics.
The founder of the Adyar Cancer Institute in India, Muthulakshmi Reddy (30 July 1886 – 22 July 1968), fought to uplift women and girls from impoverished situations.
Chinese-American virologist and molecular biologist Flossie Wong-Staal (27 August 1946 – 8 July 2020) was the first scientist to clone HIV and determine the function of its genes.
Maharani Chakravorty (1937 – 2015) was one of India’s earliest molecular biologists whose research paved the way for advances in the treatment of bacterial and viral infections.
Archana Sharma (16 February 1932 - 14 January 2008) conducted research into plant and human genetics that expanded the understanding of both botany and human health. In relation to botany, she uncovered the means by which asexually-reproducing plants evolve into new species.
The first Thai woman to receive a degree in medicine, Margaret Lin Xavier (29 May 1898 – 6 December 1932), is best remembered for her compassion towards her less privileged patients.
In 1915, pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa and his research assistant Koichi Ichikawa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
In 1915, Koichi Ichikawa along with pathologist Katsusaburo Yamagiwa became the first to prove that chronic exposure to chemicals can cause cancer.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Husband and wife team, Kimishige (3 December 1925 – 6 July 2018) and Teruko Ishizaka (28 September 1926 – 4 June 2019) discovered the antibody class Immunoglobulin E (IgE) that triggers allergic reactions. They also discovered that IgE antibodies attach to white blood cells, known as mast cells, releasing histamine, which causes allergic reactions.
Japanese chemist Takamine Jokichi (3 November 1854 – 22 July 1922) founded the Tokyo Artificial Fertilizer Company, where he isolated a starch-digesting enzyme (named takadiastase) from the fungus Aspergillus oryzae.
Ground-breaking cancer researcher Kamal Jayasing Ranadive (8 November 1917 – 11 April 2001) advanced the understanding of the causes of leukaemia, breast cancer and oesophageal cancer through the use of animal models. She was also among the first to recognise how susceptibility to cancer is linked to tumour-causing interactions between hormones and viruses.
The research of Filipino pharmaceutical chemist Luz Oliveros-Belardo (3 November 1906 – 12 December 1999) focussed on essential oils and other chemicals derived from native Philippine plants.
Thai physician and conservationist Boonsong Lekagul (1907 – 1992) made major contributions to the preservation of his country’s wildlife.
Indian scientist and physician Upendranath Brahmachari (19 December 1873–6 February 1946) is best known for creating a drug called Urea Stibamine, used to safely and reliably treat visceral leishmaniasis (or Kala-azar), a severe infection caused by the Leishmania parasite.
Filipino chemist and pharmacist Manuel A. Zamora (29 March 1870 – 9 July 1929) is best remembered for his discovery of the tiki-tiki formula to combat beriberi, a disease caused by Vitamin B1 deficiency.
Korean parasitologist Seung-Yull Cho (16 November 1943 – 27 January 2019) is remembered largely for his pioneering works to control infections caused by helminthic parasites and his contribution to journal publishing.
Fe Villanueva del Mundo (27 November 1911 – 6 August 2011) was a Filipina paediatrician who founded the Philippines’ first paediatric hospital.
After witnessing death and suffering as a youth in his home village during World War II, Nguyễn Tài Thu (6 April 1931 – 14 February 2021) set his sights on alleviating pain by becoming a doctor. After studying Traditional Chinese Medicine in China in the 1950s, Thu returned to Vietnam to serve in military hospitals. Eventually, he became the country’s foremost practitioner of acupuncture, a technique he first learned by inserting needles into himself.
Minoru Shirota (April 23, 1899 – March 10, 1982) was a Japanese microbiologist who invented the popular fermented drink Yakult.
Wu Lien-teh (10 March 1879 – 21 January 1960) was a Malaysian-born doctor who invented a mask that effectively suppressed disease transmission. Winning the prestigious Queen’s Scholarship enabled Wu to become the first Chinese student to study medicine at the University of Cambridge.
David T. Wong (born 1936) is a Hong Kong-born American neuroscientist who is best known for discovering the antidepressant drug fluoxetine, better known as Prozac.
Indian organic chemist Asima Chatterjee (1917 to 2006) studied the medicinal properties of plant products, especially compounds known as vinca alkaloids.
Chika Kuroda (24 March 1884 – 8 November 1968) was a Japanese chemist whose research focussed on the structures of natural pigments.
Umetaro Suzuki (7 April 1874 – 20 September 1943) was a Japanese scientist best remembered for his research on beriberi, a disease caused by vitamin B1 deficiency, characterized by limb stiffness, paralysis and pain.
Salimuzzaman Siddiqui (19 October 1897 – 14 April 1994) was an artist and chemist from Pakistan whose research focused on natural products from plants.
Barry Paw (29 August 1962 – 28 December 2017) was a biologist and oncologist who discovered several novel genes and their functions in red blood cells.
Syed Qasim Mehdi (13 February 1941 – 28 September 2016) was a Pakistani molecular biologist who was a founding member of the Human Genome Diversity Project (HGDP), which assessed human diversity by studying human migration, mutation rates, relationships between different populations, genes involved in height and selective pressure.
Tsai-Fan Yu (1911 – 2 March 2007) was a Chinese-American physician and researcher who was the first female full professor at Mount Sinai School of Medicine. She discovered that gout, a condition characterized by the painful inflammation of joints, was caused by elevated levels of uric acid in the bloodstream.
Min Chueh Chang (10 October 1908 – 5 June 1991) was a Chinese-American biologist who studied fertilization in mammalian reproduction.
A Japanese surgeon, Tetsuzo Akutsu (20 August 1922 – 9 August 2007) built the first artificial heart capable of keeping an animal alive.
Ogino Ginko (3 March 1851 – 23 June 1913) was the first registered female doctor to practise modern medicine in Japan.
Esther Park (1877-1910), born Kim Jeom-dong, was the first female Korean physician to practise modern medicine in Korea and trained the first generation of Korean female doctors.